Ubuntu/Debian启用rc.local
今天想使用HE Tunnel给两台服务器添加IPV6支持,在创建完隧道配置的.sh文件后试着去添加启动项,按照以往经验要去rc.local添加条目的时候却发现Debian9 /etc目录下并没有rc.local文件,随即有了下文。
在 Debian 系统中,rc.local 是一个用于在系统引导过程中执行自定义脚本的文件。然而,从 Debian 9 (Stretch) 开始,rc.local 文件默认被禁用,并且不再作为引导过程中的启动脚本。这是因为 Debian 在过渡到 systemd 初始化系统,并采用了新的引导过程。
但就目前而言,我认为rc.local的易用程度比systemd要简单方便很多,以下步骤是重新启用rc.local的方法。
1.创建rc-local.service服务,确保rc-local开机被加载
cat > /etc/systemd/system/rc-local.service <<EOF
[Unit]
Description=/etc/rc.local
ConditionPathExists=/etc/rc.local
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start
TimeoutSec=0
StandardOutput=tty
RemainAfterExit=yes
SysVStartPriority=99
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF2.在etc目录中创建rc.loacl
cat > /etc/rc.local <<EOF
#!/bin/sh -e
#
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
# bash /root/bindip.sh
exit 0
EOF3.给予权限并设置自启
chmod +x /etc/rc.local
systemctl enable rc-local
systemctl start rc-local.service4.启动服务
sudo systemctl enable rc-local.service
sudo systemctl start rc-local.service
5.检查服务状态
systemctl status rc-local.service如果服务正常启动,则会返回如图
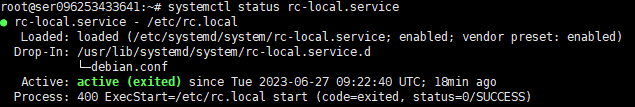
这里应该注意,rc.local中所写道的条目内容如果有错误,那么服务也会启动失败。如下图所示。
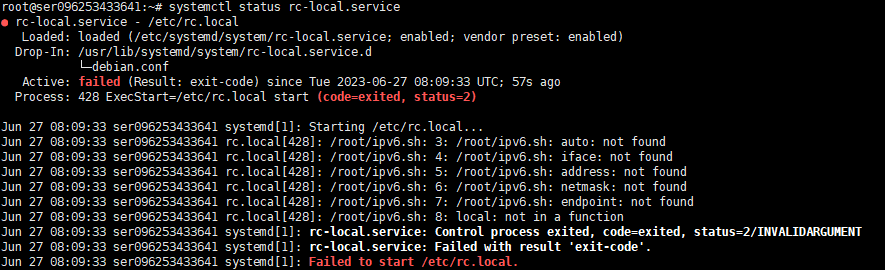
这里因为我在rc.loacl中添加了sh /root/ipv6.sh,因为ipv6.sh中的命令存在错误,所以导致服务启动失败。
需要注意的是,rc.local 在新的 Debian 系统中已经不再是推荐的方法来运行启动脚本。在 systemd 系统中,建议使用单独的单位文件(unit files)来定义和管理系统服务。如果可能的话,建议将启动脚本转换为 systemd 服务,以便更好地集成到系统中。
下面是一小部分关于systemd的内容
使用 systemd 在 Debian 系统中管理服务和执行脚本的方法:
创建一个服务单元文件(Unit File):在 /etc/systemd/system/ 目录中创建一个以 .service 结尾的文件,例如 myservice.service。
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/myservice.service编辑服务单元文件,指定服务的详细信息。一个基本的服务单元文件包括以下几个部分:
[Unit]
Description=My Service
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/path/to/my_script.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
[Unit]部分定义了服务的描述和启动顺序。[Service]部分定义了服务的执行方式。ExecStart字段指定了要执行的脚本或命令的路径。[Install]部分定义了服务的启用方式。
注意,/path/to/my_script.sh 应该替换为你要执行的脚本或命令的实际路径。
创建完成后,保存并关闭文件。接下来需要重新加载 systemd 配置。
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
启用服务:运行以下命令以在引导时自动启用服务。
sudo systemctl enable myservice
启动服务:运行以下命令以立即启动服务。
sudo systemctl start myservice现在,新添加的服务将被启动并在系统引导时自动运行。你还可以使用以下命令来管理服务:
- 启动服务:
sudo systemctl start myservice - 停止服务:
sudo systemctl stop myservice - 重启服务:
sudo systemctl restart myservice - 禁用服务:
sudo systemctl disable myservice
除此之外,你还可以使用其他 systemd 命令和选项来管理和监视服务,例如 status、enable、disable、is-active 等。可以通过 man systemd 命令查看 systemd 的完整文档以获取更多信息和用法示例。
本作品采用 知识共享署名-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可。